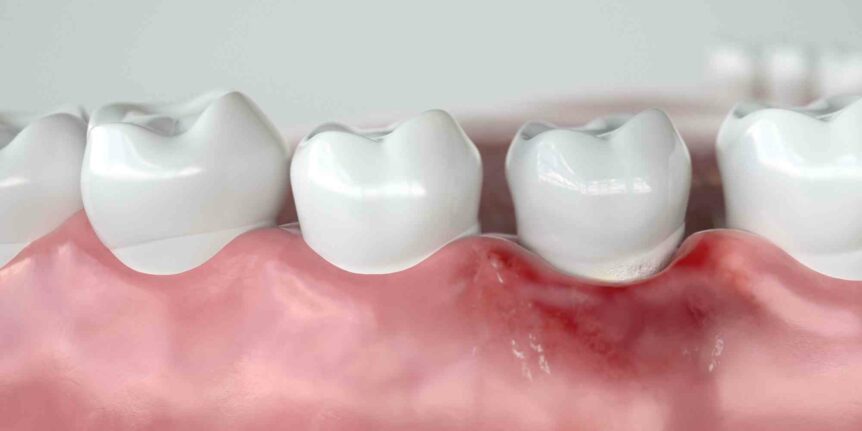
Suppose you look in the mirror and smile, and it looks as though your teeth have become longer and more prominent. If that’s the case, you may have gum recession. Receding gums are often an early sign of gum disease and can lead to serious oral health problems when the problem is ignored.
What Are Receding Gums?
Gum or gingival, recession occurs when the gums pull away from the surface of the tooth, according to the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP). More of the tooth is exposed, but some people don’t notice it right away. One of the first signs that your gums are receding might be increased sensitivity. If you eat something very hot or very cold, you may feel a sharp pain in the tooth.
You can develop receding gums for several reasons, according to the AAP. The leading cause is gum disease, but certain habits, such as brushing very vigorously or using a hard toothbrush, can make your gums more likely to recede. Habits such as smoking, grinding your teeth or wearing lip or tongue jewellery can also contribute to gum recession.
Ignoring receding gums isn’t a good idea. Left untreated, gum recession may lead to tooth loss. Receding gums treatment options depend on the severity of the recession.
Gum Graft
One surgical treatment commonly used by periodontists is gum grafting. To perform a gum graft, a periodontist takes tissue from another area and uses it to cover the exposed root and tooth area, according to the AAP. The tissue might come from the palate in your mouth or from another source. A dentist can also source the graft tissue from a tissue bank instead of from your own mouth.
Regeneration Treatment
If your gums have receded to the point that the bone has been destroyed, your periodontist might use a treatment method known as regeneration therapy to restore lost bone and gum tissue. The affected area is opened up surgically and the gum tissue is flapped back. It is deep cleaned to remove bacteria below the gum line and a protein matrix is placed on the root of the tooth. The protein will encourage the growth of new tissue attachment and new bone around the affected area to support and anchor the teeth. The periodontist will put the gum tissue back in place and stitch it after the treatment is done.
Proper oral care is essential after gum recession or regenerative treatment. If you were using a medium- or firm-bristle brush before, switch to a brush with soft bristles. Talk to your dentist or periodontist about the best way to brush and floss your teeth to prevent further recession.
Keep in touch with your periodontist after surgery. He will most likely want to see you more than twice a year. Taking the time and effort to keep your mouth in good shape will help keep receding gums at bay.